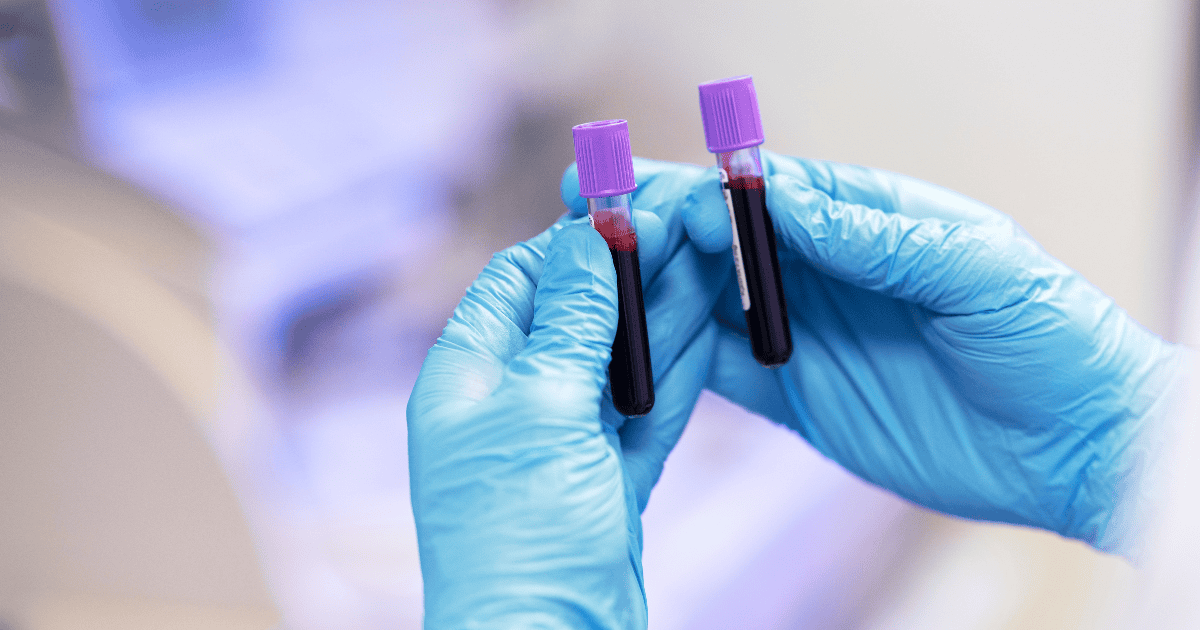
Have you ever thought, “Why was my blood so dark when drawn?” during a blood test or when a technician punctured a vein? You’re not alone. The color of blood can be surprising, especially when it appears darker than expected. Blood color is influenced by various physiological factors, including oxygen levels, hydration, and even underlying health conditions. In this article, we will explore the reasons why blood color can change, especially in clinical settings, and what it might mean for your health.
| Key Takeaways |
| Why Was My Blood So Dark When Drawn? This is usually due to lower oxygen levels in venous blood, which is normal during routine blood draws. Other factors like dehydration, increased red blood cells, or underlying health conditions can also affect blood color. |
| Oxygen Saturation Matters: Blood with lower oxygen levels will naturally appear darker. Respiratory issues or circulatory problems may cause darker blood during phlebotomy. |
| Dehydration: Not drinking enough fluids can make your blood more concentrated and appear darker. |
| Medical Conditions: Certain health issues, like inflammation, can cause darker blood. In some cases, it can be a sign of a more serious medical problem, especially in patients with chronic illnesses. |
| Phlebotomist Tips: Reassuring patients, encouraging hydration, and knowing when to escalate potential concerns are critical for providing quality care. |
What Determines Blood Color?
The color of blood is mainly influenced by its oxygen content. Bright red blood is typically rich in oxygen and comes from the arteries, which transport oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body. On the other hand, venous blood, which is returning to the heart after delivering oxygen to tissues, tends to be darker due to its lower oxygen levels.
This physiological difference explains why the blood drawn during routine tests often appears darker—it is usually taken from a vein, where oxygen levels are naturally lower.
However, blood color can also be influenced by several other factors, including hydration, circulation, and health conditions. Let’s explore these factors further.
Key Factors That Can Cause Darker Blood During a Blood Draw
- Oxygen Saturation Levels
- Blood’s color is directly related to how much oxygen it contains. If your blood has a lower oxygen saturation, it will appear darker. This is common when venous blood is drawn because venous blood is deoxygenated after its journey through the body. People with respiratory issues or poor oxygenation may notice darker blood when they have their blood drawn.
- Dehydration
- Dehydration is another common cause of darker blood. When you are dehydrated, your blood volume decreases, and the remaining blood becomes more concentrated. This concentration gives blood a darker, thicker appearance during a blood draw. Hydration is essential for maintaining normal blood flow and a healthy appearance.
- Increased Red Blood Cell Count
- Conditions like polycythemia vera, where the body produces too many red blood cells, can make blood appear darker. In these cases, the increased concentration of hemoglobin can give the blood a thicker, more viscous appearance, which may be noticeable during phlebotomy procedures.
- Inflammation and Infections
- According to a study by Shibata et al., darkened blood color can be linked to inflammation, as seen in patients with elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Infections or other inflammatory conditions can affect blood color, making it appear darker than usual during a blood draw.
- Poor Circulation
- People with circulatory issues, such as those with heart or vascular problems, may experience slower blood flow, which can cause the blood to darken due to reduced oxygen exchange. Poor circulation can make it more difficult for oxygen to reach tissues, causing blood to take on a darker hue.
- Altitude and Air Quality
- If you’ve recently been in a high-altitude environment, the reduced oxygen levels in the atmosphere can lower the oxygen saturation in your blood. This leads to darker blood being drawn. Similarly, poor air quality or respiratory conditions can reduce the oxygen content in the blood, affecting its color.
Why Was My Blood So Dark When Drawn? Key Medical Insights
In some cases, darker blood may point to specific medical conditions. For instance, patients undergoing dialysis often experience changes in blood color due to inflammation and oxygenation issues. Research conducted by Shibata et al. on hemodialysis patients found that darker blood color could predict survival outcomes. The study suggested that blood color darkness, influenced by factors like C-reactive protein levels and white blood cell count, was linked to poorer survival rates in critically ill patients.
This highlights that while darker blood can often be benign, in some medical contexts, it could be a warning sign of underlying health problems such as chronic inflammation or poor oxygenation. For phlebotomy professionals, it’s crucial to be aware of these factors and provide the appropriate care when drawing blood from patients.
Phlebotomy Best Practices When Drawing Dark Blood
For phlebotomists, encountering dark blood during a blood draw can be a routine experience, but it’s important to know how to manage this situation professionally:
- Reassuring the Patient:
Many patients may be alarmed if they notice their blood is darker than usual. It’s essential to explain that venous blood is often darker due to its low oxygen content and that this is normal during a blood draw. Offering clear, calm explanations can ease a patient’s concerns. - Encouraging Hydration:
Ensuring that patients are properly hydrated before a blood draw can help reduce the risk of dehydration-induced darker blood. Always remind patients to drink water before their appointment. - Monitoring for Other Symptoms:
If dark blood is accompanied by other symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, or fatigue, it may indicate an underlying health issue. Phlebotomists should inform patients to consult a healthcare provider if these symptoms are present. - Knowing When to Escalate:
In cases where dark blood may indicate a medical issue, such as circulatory problems or inflammation, it’s crucial to follow up with the patient’s healthcare team. Proper documentation and communication are key in ensuring that the patient receives the right care.
When Should You Be Concerned About Dark Blood?
While darker blood is typically nothing to worry about, especially in the context of a routine blood draw, there are some cases where it might warrant further investigation. Patients with existing health conditions such as anemia, cardiovascular disease, or chronic respiratory issues may need to pay closer attention to blood color changes.
If you notice that your blood is consistently dark during draws and you’re experiencing symptoms like extreme fatigue, shortness of breath, or unexplained weight loss, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Early detection of potential health issues can lead to better outcomes.
FAQs
Is dark blood during a blood draw something to worry about?
In most cases, darker blood during a blood draw is normal, especially if it is venous blood. However, if it is accompanied by other symptoms or if you have a chronic health condition, it may require further investigation.
Why does dehydration cause darker blood?
Dehydration reduces blood volume, making your blood more concentrated and giving it a darker appearance. Staying hydrated before a blood draw can help prevent this.
Can certain diseases cause my blood to appear darker?
Yes, conditions like polycythemia vera, poor circulation, or inflammation can cause darker blood. If you have an underlying health issue, darker blood may be a sign to consult with your healthcare provider.
Should I drink water before a blood draw?
Yes, drinking water before a blood draw can help ensure your blood flows easily and maintains its normal appearance. Hydration also helps phlebotomists get a cleaner, easier draw.
What should I do if I notice my blood is consistently dark?
If your blood is consistently dark during blood draws and you’re experiencing symptoms like fatigue or shortness of breath, consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Conclusion: Understanding the Significance of Dark Blood in Phlebotomy
So, why was my blood so dark when drawn? While it can be disconcerting to see darker blood, it is usually due to normal physiological reasons like lower oxygen levels in venous blood, dehydration, or other manageable factors. However, in some cases, darker blood can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, particularly in patients with chronic health issues or those undergoing treatments like dialysis.
Phlebotomy professionals should be equipped with the knowledge to both understand the significance of darker blood and reassure patients that, in most cases, it’s a normal part of the blood draw process.
Start Your Phlebotomy Career with Phlebotomy Now School in Texas!
Ready to become a skilled phlebotomist? Phlebotomy Now School in Texas offers hands-on training, flexible classes, and expert guidance to help you get certified fast.
Enroll today and take the first step toward a rewarding healthcare career!