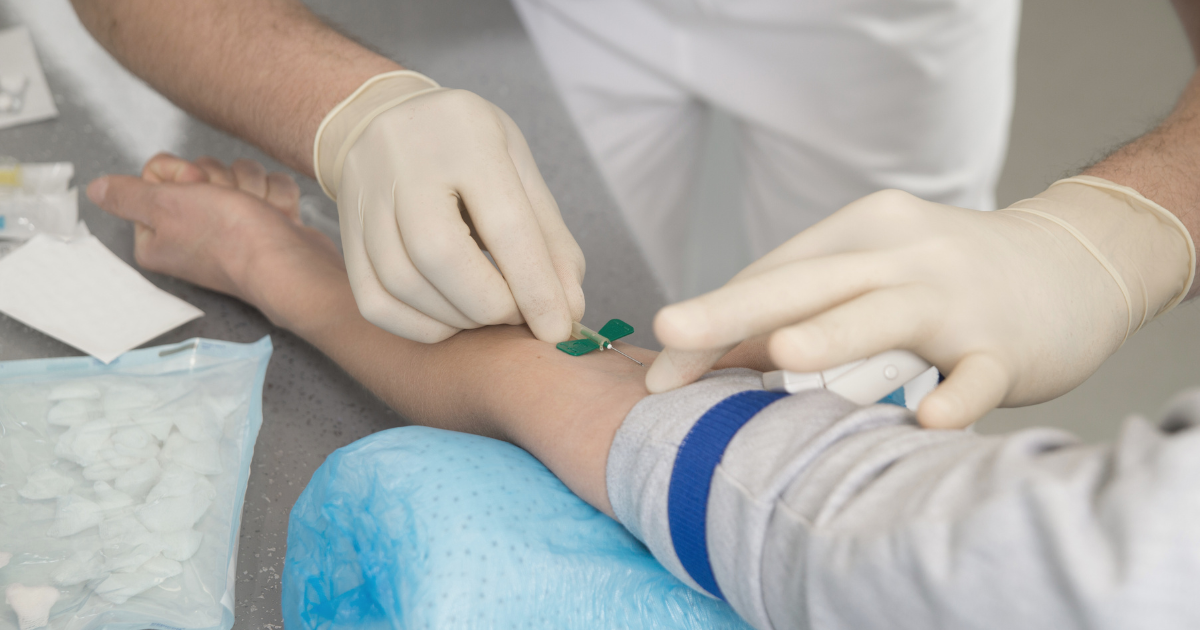
Experiencing a needle in vein but no blood can be both frustrating and concerning, especially in medical settings where timely and efficient blood collection is crucial. This article delves into the potential causes and solutions for this common issue, providing valuable insights for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
| Key Takeaways |
| Understanding Vein Anatomy: Knowledge of vein anatomy is crucial for successful blood draws and preventing needle in vein but no blood situations. |
| Common Causes: Blocked veins, low blood pressure, incorrect needle angle, and patient anxiety are frequent causes of needle in vein but no blood. |
| Effective Techniques: Applying warm compresses, using thinner needles, adjusting needle angles, and managing patient anxiety can enhance blood draw success. |
| Alternative Solutions: If initial attempts fail, alternative sites and advanced techniques can be employed to avoid needle in vein but no blood issues. |
| Seek Medical Help: Persistent difficulties in drawing blood should prompt medical evaluation to identify and address underlying issues. |
If you’re in a hurry, here’s a quick overview: difficulty in drawing blood or getting no blood return can stem from various factors such as vein scarring, blockages, collapsed veins, low blood pressure, incorrect needle angle, and more. Solutions include adjusting the needle position, using a smaller needle, applying warm compresses to enhance circulation, or locating an alternative site.
In the sections below, we will explore the anatomy behind blood draws, reasons for no blood return, and troubleshooting tips for successful venipuncture. This content is particularly aimed at students and professionals in the medical field, and it employs a formal yet approachable tone. The search intent for this article is informational.
Anatomy Behind Drawing Blood
Understanding the anatomy behind blood draws is essential for healthcare professionals to efficiently collect blood samples. The process involves accessing veins, which are responsible for returning blood to the heart.
How Blood Flows Through Veins
When drawing blood, a needle is inserted into a vein, allowing for the collection of a blood sample. Blood flow in veins relies on several factors:
- Skeletal Muscle Contraction: Surrounding muscles contract to push blood towards the heart.
- Valves in Veins: These prevent blood from flowing backward, ensuring unidirectional flow towards the heart.
Factors Making Veins More Difficult to Access
Several factors can complicate vein access:
- Dehydration, Obesity, and Age: These conditions can make veins less prominent and harder to locate.
- Vein Size and Condition: Smaller or more fragile veins are more challenging to puncture.
- Scarring and Medical Conditions: Scar tissue from repeated procedures or conditions like thrombosis or phlebitis can obstruct veins.
Common Reasons for Needle in Vein But No Blood
Blocked or Damaged Veins
Repeated medical procedures or conditions like thrombosis can lead to vein blockages or damage, making blood collection difficult. Scar tissue from previous procedures can also obstruct veins, resulting in a needle in vein but no blood situation.
Low Blood Pressure
Low blood pressure can hinder blood flow into the needle. Dehydration or medical conditions like hypotension can exacerbate this issue, necessitating measures to increase blood pressure for successful blood draws.
Needle Angle and Depth Issues
Incorrect needle angle or depth can prevent proper vein access. Proper training and technique are crucial to ensure correct needle placement and avoid situations where there is a needle in vein but no blood.
Arm Positioning
Incorrect arm positioning can impede blood flow or make vein access difficult. A relaxed and extended arm position is essential for successful blood draws, preventing scenarios of needle in vein but no blood.
Small or Rolling Veins
Small veins are harder to access, and rolling veins can move away from the needle. Using a smaller needle or applying gentle pressure can help in these cases, reducing the instances of needle in vein but no blood.
Patient Anxiety and Vasovagal Response
Anxiety can trigger a vasovagal response, reducing blood flow and complicating blood draws. Techniques to alleviate anxiety, such as deep breathing or distraction, can improve blood return and prevent the needle in vein but no blood issue.
Tips for Improving Blood Draw Success
Apply Warm Compresses
Applying a warm compress to the area before attempting a blood draw can dilate blood vessels, making veins easier to locate and access. This can help avoid the needle in vein but no blood problem.
Use Thinner Needle Gauge
Thinner needles can reduce discomfort and are easier to maneuver into veins. Selecting the appropriate needle gauge based on the patient’s vein condition is crucial to prevent needle in vein but no blood situations.
Adjust Needle Angle and Depth
Healthcare professionals should adjust the needle angle and depth as needed to ensure proper vein access and blood return, avoiding the issue of needle in vein but no blood.
Find Alternative Site
If a vein is difficult to access, alternative sites like the back of the hand or forearm can be considered. Knowledge of different sites and their suitability is essential to prevent needle in vein but no blood scenarios.
Have Patient Open and Close Fist
Instructing the patient to open and close their fist can increase blood flow and make veins more prominent, facilitating easier access and avoiding needle in vein but no blood situations.
Use Vein Visualization Tools
Vein visualization tools using infrared light can help locate veins, improving the success rate of blood draws and reducing the occurrence of needle in vein but no blood issues.
Manage Patient’s Anxiety
Explaining the procedure, offering reassurance, and providing a calm environment can help reduce patient anxiety and facilitate blood draws, preventing needle in vein but no blood problems.
Consider Different Draw Tubes
Different draw tubes have varying additives and properties that can affect blood flow. Using alternative draw tubes may be beneficial if initial attempts are unsuccessful, avoiding the needle in vein but no blood issue.
When to Seek Medical Care for Difficult Blood Draws
Causes of Difficult Blood Draws
Factors like dehydration, obesity, small or fragile veins, scar tissue, and medical conditions like diabetes or blood clotting disorders can contribute to difficult blood draws and needle in vein but no blood situations. Certain medications can also affect blood clotting and complicate the process.
Signs to Look Out For
Seek medical care if you experience:
- Excessive pain or discomfort
- Persistent bleeding or hematoma formation
- Inability to locate or access a vein
- Repeated unsuccessful attempts
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
These signs may indicate complications or underlying issues requiring further evaluation and management.
Solutions and When to Seek Medical Care
Communicate concerns to the healthcare provider, who may try different techniques or equipment. If unsuccessful, consult a phlebotomist or vascular access specialist. Advanced techniques like ultrasound-guided venipuncture or alternative methods such as butterfly needles may be necessary.
FAQs
What should I do if the needle is in the vein but no blood is coming out?
Try adjusting the needle angle and depth, apply a warm compress, or ask the patient to open and close their fist. If these methods fail, consider using a smaller needle or finding an alternative site.
Why is my vein not giving blood?
Common reasons include blocked or damaged veins, low blood pressure, incorrect needle insertion technique, and patient anxiety. Identifying the cause can help determine the appropriate solution.
How can I prevent needle in vein but no blood situations?
Proper training in needle insertion, using appropriate equipment, and techniques like warm compresses and vein visualization tools can prevent this issue.
When should I seek medical care for difficult blood draws?
Seek medical care if there is excessive pain, persistent bleeding, repeated unsuccessful attempts, or symptoms like fainting. Medical evaluation can help address underlying problems.
Can patient anxiety affect blood draws?
Yes, anxiety can trigger a vasovagal response, reducing blood flow and complicating blood draws. Managing patient anxiety through reassurance and relaxation techniques can improve outcomes.
Difficulty drawing blood, especially when the needle is in the vein but no blood is returning, can be a frustrating experience for both healthcare professionals and patients. Understanding the underlying causes, such as blocked veins, low blood pressure, and improper technique, is key to addressing the issue.
By applying warm compresses, using finer needles, adjusting needle angles, and managing patient anxiety, blood draws can become more straightforward. Persistent difficulty may require medical evaluation to identify any underlying conditions.
With proper care and technique, successful blood draws can be achieved, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of medical care.
Ready to master venipuncture? Join Phlebotomy Now School today!
Our expert courses will equip you with the skills for successful blood draws every time.
Enroll Now at Phlebotomy Now School! Enhance your phlebotomy skills and advance your medical career.