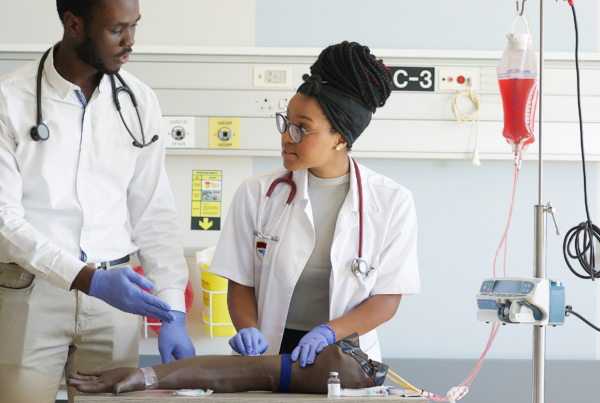
This comprehensive guide is designed for aspiring phlebotomists seeking to master the phlebotomy procedure. We’ll delve into the essential steps, crucial skills, and helpful techniques to ensure successful blood draws while prioritizing patient comfort and safety.
| Key Takeaways: Phlebotomy Procedure |
| Mastering the phlebotomy procedure requires a combination of technical skills, patient care, and effective communication. |
| Careful attention to detail throughout each step ensures patient safety and accurate blood collection. |
| Phlebotomy training programs equip aspiring phlebotomists with the knowledge and skills necessary for success in this field. |
Why is Phlebotomy Important?
Phlebotomy plays a vital role in modern healthcare. By skillfully collecting blood samples, phlebotomists contribute to a wide range of medical diagnosis and treatment plans. A successful blood draw ensures accurate test results, ultimately impacting patient care.
Mastering the Phlebotomy Procedure: Step-by-Step
The phlebotomy procedure involves a series of critical steps that must be followed meticulously. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Patient Identification and Order Verification: Confirm the patient’s identity matches the paperwork and ensure the requested tests are accurate. This reduces errors and unnecessary blood draws.
- Patient Communication: Before starting, establish rapport with the patient. Briefly explain the procedure and address any questions or anxieties.
- Hand Hygiene: Demonstrate professionalism and prioritize patient safety by thoroughly washing your hands for at least 20 seconds with soap and water in front of the patient.
- Preparation of Supplies: Gather all necessary supplies near the patient, including needles, tubes, tourniquet, alcohol swabs, gauze pads, and gloves. Remove sterile equipment from packaging only when ready for use.
- Selecting the Venipuncture Site: Choose an appropriate arm for blood draw and apply the tourniquet comfortably but not too tightly, avoiding prolonged application to prevent injury.
- Vein Localization: Palpate the arm to locate a suitable vein. Experience aids in identifying easily accessible veins.
- Site Disinfection: Disinfect the chosen puncture site with an alcohol wipe followed by a sterile gauze pad to create a clean area for needle insertion.
- Needle Insertion: Anchor the vein with your thumb below the puncture site. Insert the needle at a 15-degree angle into the vein with a smooth, swift motion.
- Blood Collection: Attach the blood collection tube to the needle hub and ensure proper blood flow. Once the tube fills, carefully remove it. Gently invert the tube 5-10 times to mix the blood without shaking.
- Multiple Tube Collection: Repeat steps 12-13 to fill all required tubes as per the order.
- Patient Monitoring: Throughout the procedure, check in with the patient to ensure their comfort and address any concerns.
- Tube Removal and Disposal: After filling the last tube, keep it attached to the hub. Release the tourniquet, then remove and invert the tube.
- Needle Removal and Disposal: Safely remove the needle and apply firm pressure with gauze to the puncture site to stop bleeding. Activate the needle’s safety mechanism and dispose of it properly in a designated sharps container.
- Specimen Labeling: Meticulously label all blood collection tubes with the patient’s name, date of birth, and other required identifiers to ensure accurate sample tracking.
- Bandaging and Aftercare: Apply a bandage over the puncture site once bleeding stops. Dispose of all medical waste appropriately.
- Patient Observation: Briefly monitor the patient after the procedure, checking for signs of dizziness or discomfort. Offer water or a light snack if needed, and allow them to rest for a few moments.
Challenges and Solutions: Finding Difficult Veins
Some patients may have veins that are difficult to locate due to various factors. Here are techniques to overcome challenges:
- Palpation Techniques: Develop skilled palpation techniques to effectively locate suitable veins.
- Tourniquet Use: The tourniquet can temporarily increase vein visibility, but avoid prolonged application to prevent injury.
- Light Technique: Using a flashlight can help illuminate veins beneath the skin’s surface.
- Patient History: Inquire about the patient’s blood draw history. Knowing if specific veins were used previously can guide your approach.
- Seeking Assistance: If difficulty persists, don’t hesitate to consult a more experienced phlebotomist for assistance.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Phlebotomy skills are honed through consistent practice. Many phlebotomy training programs incorporate hands-on learning in clinical settings.
- Calm Demeanor: Patients often experience anxiety during blood draws. Maintaining a calm and reassuring demeanor helps ease their worries and fosters a positive experience.
- Communication is Key: Clear communication with the patient throughout the procedure builds trust and reduces stress. Explain each step simply and address any questions they may have.
- Professionalism Matters: Dress professionally and maintain a clean, well-organized workspace. This conveys competence and instills confidence in the patient.
Choosing the Right Phlebotomy Training
Enrolling in a reputable phlebotomy training program equips you with the necessary knowledge and skills to excel in this field. Look for programs accredited by national organizations to ensure you receive high-quality education.
Phlebotomy Now : Your Path to Success
Phlebotomy Now is a nationally accredited phlebotomy training program designed to prepare you for a rewarding career in phlebotomy. Our comprehensive curriculum covers all aspects of the phlebotomy procedure, from proper blood collection techniques to patient care and communication.
Phlebotomy Now Offers:
- Certified Phlebotomy Technician Program: This program provides the foundation for your phlebotomy career, equipping you with the skills and knowledge to perform safe and efficient blood draws.
- Hands-on Training: We prioritize practical experience through simulated labs and clinical rotations under the guidance of experienced instructors.
- Career Services: Phlebotomy Now is dedicated to your success. Our career services team provides personalized guidance and support in finding your dream phlebotomy job.
FAQs
Is phlebotomy a good career choice?
Yes, phlebotomy is a growing field with a positive job outlook. It offers a rewarding career path for those who enjoy working in healthcare and helping others.
What skills are needed to become a phlebotomist?
Phlebotomists need strong technical skills for blood collection, as well as excellent communication and interpersonal skills to ensure patient comfort.
How much time is required to train as a phlebotomist?
Phlebotomy training programs typically take a few months to complete.
What sets a phlebotomist apart from a nurse?
Nurses have a broader scope of practice and can perform a wider range of tasks compared to phlebotomists who specialize in blood collection.
Where can phlebotomists work?
Phlebotomists can find employment in hospitals, clinics, doctor’s offices, blood donation centers, and other healthcare settings.
Disclaimer: The guide provides information for learning. It is not medical advice. Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any questions or concerns you may have regarding phlebotomy procedures.
Ready to Take the First Step?
If you’re passionate about a career in healthcare and helping others, phlebotomy may be the perfect path for you. Contact Phlebotomy Now today to learn more about our programs and how we can help you achieve your goals in this rewarding field.
We offer flexible scheduling and experienced instructors to guide you every step of the way.